Understanding Credentials and OAuth in Workflow Automation
Last updated: February 2026
Credentials are securely stored authentication profiles that hold your login information, API keys, and authorization tokens. OAuth is an authorization protocol that allows systems to verify identity and grant limited access without sharing passwords.
When you build automation workflows, security becomes critical. Your automations need access to Gmail, QuickBooks, Google Sheets, and dozens of other applications. But how do you grant this access safely?
The answer lies in understanding two fundamental concepts: credentials and OAuth. These security mechanisms protect your data while enabling seamless automation across platforms.
Key Takeaways
- Credentials store your authentication data securely on automation platforms
- OAuth authorizes access without sharing actual passwords
- Both systems enable reusable, secure connections across multiple workflows
- Proper credential management prevents security vulnerabilities in automation
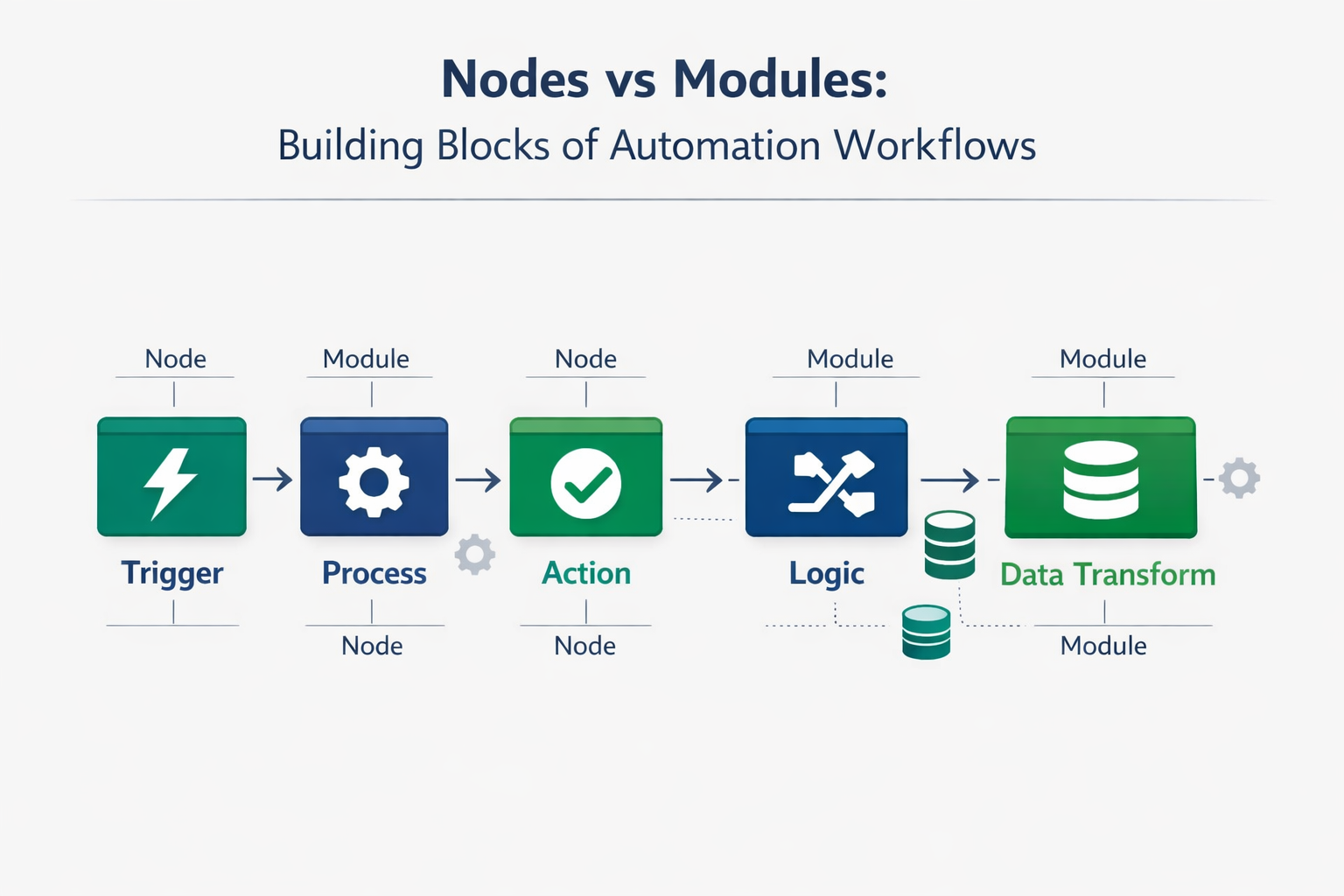
What Are Credentials in Automation?
Authentication Data
Username/email and password combinations that grant access to your cloud applications and services.
API Keys & Tokens
Secure keys that applications use to authenticate API requests without exposing passwords.
Reusable Profiles
Stored authentication profiles that work across multiple workflows without re-entering login details.
Think about your daily routine. You log into Gmail, check QuickBooks, update Google Sheets, and access your bank account. Each login requires entering your username and password.
In automation, this process happens hundreds of times per day across different workflows. Manually entering credentials each time would make automation impossible.
Credentials solve this by storing your authentication data securely on platforms like Make, Zapier, or n8n. The platform encrypts and stores your login information, then uses it to authenticate your workflows automatically.
How Credential Storage Works
Enter Credentials
One-time setup
Secure Encryption
Platform encrypts data
Reuse Everywhere
All workflows access
When you create 10 workflows that all connect to Google Sheets, you don’t enter your Google credentials 10 times. You create one credential profile and reuse it across all workflows.
Understanding OAuth Authentication
OAuth (Open Authorization) is a security protocol that solves a critical problem: How do you grant access without sharing passwords?
Imagine someone knocks on your door claiming to install your air conditioner. You wouldn’t just let them in. You’d ask for identification, verify they’re scheduled, maybe call the company to confirm.
OAuth works similarly for applications. It’s a verification system that confirms identity before granting access.
Important:
OAuth allows third-party applications limited access to your resources without ever seeing your actual passwords. Your credentials remain secure with the original service provider.
The OAuth Authorization Flow
Step 1: Authorization Request
Your automation platform requests permission to access your Google account, QuickBooks data, or other service.
Step 2: User Consent
You’re redirected to the actual service (Google, QuickBooks) to log in and grant specific permissions.
Step 3: Authorization Token
The service issues a secure token that grants limited access without exposing your password.
Step 4: Secure Access
Your automation platform uses the token to access only the specific data and functions you authorized.
Platform Implementation Examples
Different automation platforms handle credentials and OAuth in similar ways, but with platform-specific interfaces.
| Platform | Credential Storage | OAuth Support |
|---|---|---|
| Make.com | Connection profiles with encryption | Built-in OAuth for 1000+ services |
| Zapier | App connections with secure tokens | OAuth 2.0 for major platforms |
| n8n | Credential management system | OAuth 1.0 and 2.0 support |
| Microsoft Power Automate | Connection references | Azure AD OAuth integration |
Setting Up Secure Connections
Choose Authentication Method
Select OAuth when available, API key for developer tools, or basic auth for legacy systems.
Grant Minimal Permissions
Only authorize the specific data access and actions your workflows actually need.
Test Connection Security
Verify that credentials work properly and review what data the automation can access.
Monitor & Maintain
Regular audits of active connections and prompt updates when tokens expire.
Common Security Mistakes and Solutions
| Security Mistake | Secure Solution |
|---|---|
| Sharing login credentials across team members | Create individual OAuth connections for each team member |
| Granting full account access when limited access is sufficient | Review and minimize OAuth scope permissions during setup |
| Never reviewing or revoking old connections | Quarterly audit of active connections and remove unused ones |
| Using the same credentials across multiple platforms | Create platform-specific credentials with unique passwords |
| Ignoring expired token notifications | Set up monitoring alerts and refresh tokens promptly |
Example Authentication Scenarios
Here are real-world examples of how credentials and OAuth work in common automation workflows:
OAuth for Google Sheets read access + SMTP credentials for email sending
API key for CRM data + OAuth for QuickBooks invoice creation
Webhook for form submission + OAuth for Slack channel posting
Database connection string + OAuth for Google Drive file upload
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between credentials and OAuth?
Credentials are the stored authentication data (usernames, passwords, API keys). OAuth is the protocol that safely exchanges these credentials for secure access tokens without exposing your actual passwords.
Can I use the same credentials across multiple automation platforms?
While technically possible, it’s not recommended for security. Each platform should have its own credential set. However, you can use the same OAuth authorizations if the service provider supports multiple connected applications.
How often do OAuth tokens expire?
It varies by service provider. Google tokens typically last 1 hour but refresh automatically. Some services offer tokens that last weeks or months. Most automation platforms handle token refresh automatically.
What happens if my credentials are compromised?
Immediately revoke access from the original service provider (Google, Microsoft, etc.), change your passwords, and recreate the connections in your automation platform. Monitor for any unauthorized activity.
Should I use OAuth or API keys when both are available?
Choose OAuth when available as it’s more secure and offers better permission control. Use API keys for developer tools and services that don’t support OAuth, but store them as securely as possible.
How do I audit my automation platform connections?
Check your platform’s connection or credential management section quarterly. Also review connected apps in each service provider (Google Account, Microsoft Account, etc.) and revoke any unused connections.
Can team members share OAuth connections?
It depends on your platform and security needs. Some platforms support shared team credentials, while others require individual connections. Individual connections provide better audit trails and security isolation.
What permissions should I grant during OAuth setup?
Follow the principle of least privilege. Only grant the minimum permissions needed for your specific workflows. For example, if you only need to read spreadsheet data, don’t grant write or delete permissions.
How do I troubleshoot failed authentication in workflows?
Check if tokens have expired, verify the connection still exists in your platform, confirm the service provider hasn’t changed API requirements, and test the connection with a simple workflow first.
Ready to Secure Your Automation Workflows?
Proper credential management and OAuth implementation are crucial for automation security. Don’t let poor authentication practices expose your business data.
Vimaxus helps SMBs and service providers implement secure, scalable automation workflows with proper credential management and OAuth best practices.
Author: Viktoriia Didur, AI Automation Consultant
Published by: Vimaxus
Sources & Additional Reading
- OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework – RFC 6749
- Platform-specific credential management documentation
- Industry best practices for API security