Nodes vs Modules: Building Blocks of Automation Workflows
Last updated: February 2026
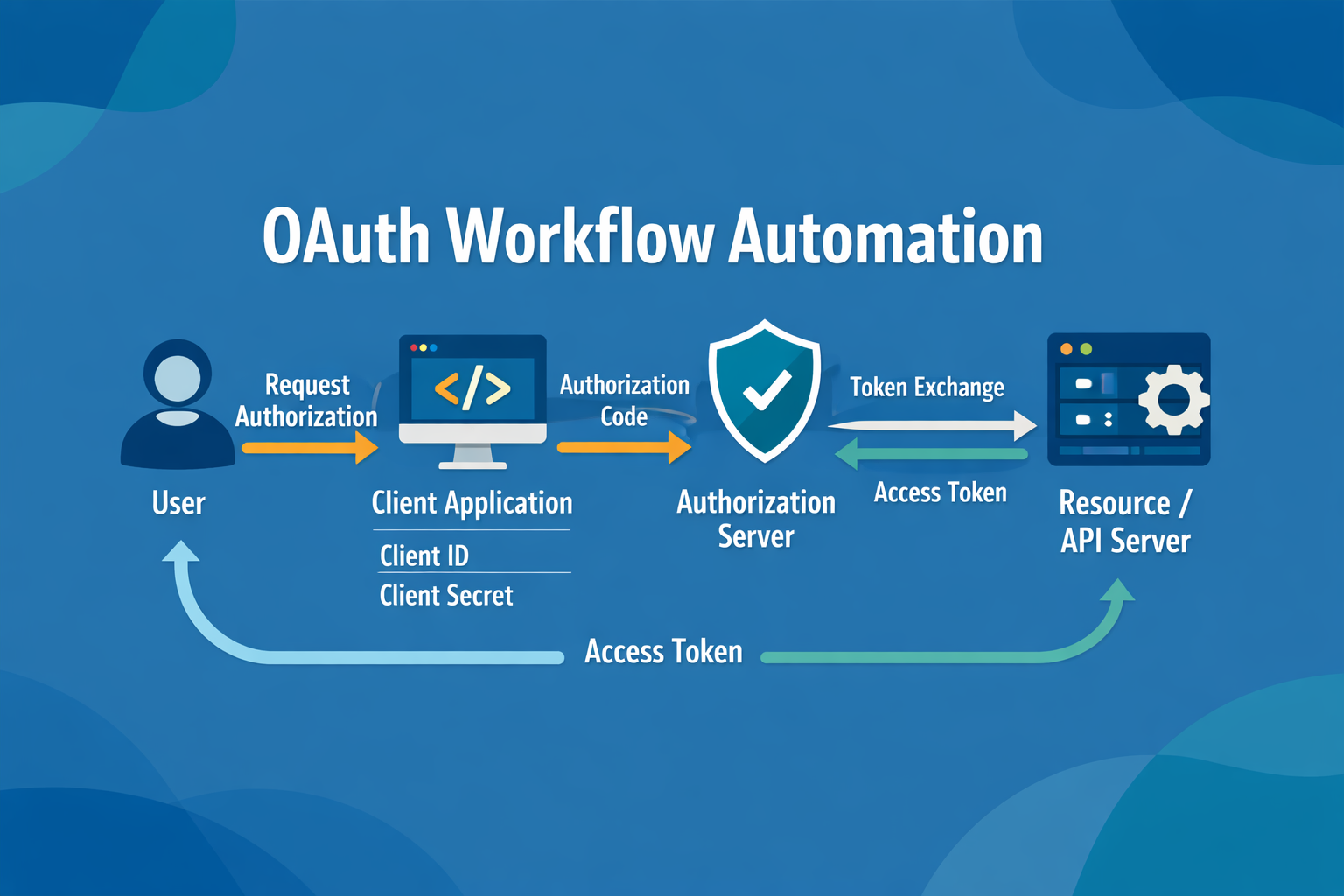
Nodes and modules are individual action blocks that perform specific tasks in automation platforms. Each node represents one step in your workflow, connecting together to create automated processes that handle everything from email management to data processing.
Every automation workflow you build starts with understanding its fundamental building blocks. Whether you call them nodes, modules, or action blocks, these components form the foundation of how automation platforms like Make, Zapier, and N8N operate.
Think about how you naturally break down complex tasks. When teaching a child to plan their work, you help them divide big projects into smaller, manageable steps. Automation platforms work the same way.
Quick Summary
- Nodes are individual action blocks that perform one specific task
- Different platforms use different terms: Make calls them modules, Zapier calls automations “zaps”
- Visual drag-and-drop builders let you connect nodes to create workflows
- Each node connects to others, forming complete automated processes
What Nodes and Modules Actually Mean
The terminology can be confusing when you’re starting with automation platforms. Here’s how different platforms refer to their building blocks:
Nodes
Individual action blocks that perform one specific task. The universal term used across most automation platforms to describe workflow components.
Modules
Make.com’s specific term for nodes. Each module represents one action or trigger in your automation scenario.
Action Blocks
Another common term describing the same concept. Each block performs one action in your automated workflow.
How Automation Workflows Connect
Understanding how nodes connect is crucial for building effective automations. Here’s the typical flow structure:
Trigger Node
Starts the workflow
Processing Node
Transforms data
Action Node
Executes final task
Building Workflows with Visual Builders
Modern automation platforms use drag-and-drop visual builders that make connecting nodes intuitive. Here’s what you’ll encounter:
Canvas Interface
The main workspace where you build your automation. It starts with a single “plus” button where you add your first node.
- Click the plus button to add nodes
- Drag to connect nodes in sequence
- Visual lines show data flow between components
- Test functionality with real data
Node Configuration
Each node requires specific settings to function properly. Configuration varies by service and action type.
- Authentication credentials for connected services
- Specific actions (create, update, delete, search)
- Data mapping between different nodes
- Conditional logic and filters
Platform-Specific Terminology
Each automation platform has its own vocabulary, but the concepts remain consistent. Here’s how major platforms organize their workflows:
Building Your First Workflow
Starting with a new automation scenario follows a predictable pattern across all platforms. Here’s the step-by-step process:
Start with Trigger
Choose what event will start your automation. This could be a new email, form submission, or scheduled time.
Add Processing
Connect nodes that transform, filter, or analyze your data. This might include AI processing or data formatting.
Execute Actions
Finish with nodes that perform final actions like sending emails, updating spreadsheets, or creating records.
Test and Deploy
Run your workflow with test data to ensure everything works correctly before activating it for live use.
Common Node Types and Functions
Most automation platforms organize nodes into similar categories. Understanding these types helps you plan workflows more effectively:
Important:
Not all automations need AI components. In fact, 60 to 80% of effective business automations work perfectly without any AI processing, focusing instead on data movement and basic logic.
Sample Workflow Queries
Here are common automation scenarios you might want to build, showing how nodes connect in real workflows:
Gmail trigger → OpenAI processing → Slack notificationForm submission → Data validation → CRM record creationSchedule trigger → Database query → Email reportWebhook → Content processing → Multiple social postsNew file → OCR extraction → Spreadsheet updateCustomer signup → Welcome sequence → Analytics trackingWhat’s the difference between nodes and modules?
Nodes and modules are essentially the same thing. “Node” is the universal term used across most automation platforms, while “modules” is Make.com’s specific terminology. Both refer to individual action blocks that perform one specific task in your workflow.
How many nodes can I connect in one workflow?
The number of nodes you can connect depends on your platform’s limits and your subscription plan. Most platforms support hundreds of nodes per workflow, but performance may slow with very complex automations. For optimal performance, keep workflows focused on specific tasks.
Do I need AI in every automation workflow?
No, most business automations work perfectly without AI. Data shows 60 to 80% of effective automations focus on data movement, formatting, and basic logic rather than AI processing. Only add AI nodes when you specifically need content generation, analysis, or complex decision-making.
What happens if one node fails in my workflow?
When a node fails, most platforms stop the workflow execution at that point and send you an error notification. You can configure error handling nodes to catch failures and take alternative actions, like logging errors or sending notifications to your team.
Can nodes run in parallel or only in sequence?
Most modern automation platforms support both sequential and parallel execution. You can use router or splitter nodes to run multiple branches simultaneously, then merge results later in your workflow. This is useful for processing multiple data sources or performing concurrent actions.
How do I test individual nodes before activating my workflow?
All major automation platforms include testing features. You can run individual nodes with sample data, execute partial workflows, and use debug modes to see data passing between nodes. Always test with real data before activating your automation for production use.
What’s the cost structure for using multiple nodes?
Most automation platforms charge based on “operations” or “tasks” rather than the number of nodes. Each time a node executes, it counts as one operation. Pricing varies by platform and subscription tier, with higher plans offering more monthly operations and advanced features.
Can I reuse nodes across different workflows?
While you can’t directly copy individual nodes, most platforms let you duplicate entire workflows or workflow segments. You can also create templates of common node configurations and save them for reuse in future automations.
Ready to Build Your First Automation?
Understanding nodes and modules is just the beginning. The real power comes from connecting them strategically to solve your business challenges.
Expert AI Automation Consulting
Viktoriia Didur helps SMBs and service providers implement automation workflows that actually work. Get personalized guidance on choosing the right platforms and connecting nodes for maximum efficiency.
About the Author
Viktoriia Didur is an AI Automation Consultant at Vimaxus, specializing in helping businesses implement effective automation workflows. She focuses on practical, results-driven solutions that eliminate manual tasks and improve operational efficiency.
Sources
- Live demonstration of Make.com automation platform interface and terminology
- Platform comparison data from Make, Zapier, N8N, and Power Automate documentation
- Vimaxus client automation usage patterns and statistics